Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF)
In any spinal fusion, two or more vertebrae are fixed in position and stabilized after a degenerated disc is removed so they become, essentially, a single unit. They are held in position using hardware — screws, rods, and a “cage” — that prevents them from moving independently and causing pain. Traditionally, a neurosurgeon would make an incision in the patient’s back to reach the vertebrae that need to be fused. In an anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) procedure, the neurosurgeon makes the incision on the front (anterior) side of the patient, and in a lateral interbody fusion (LLIF) the incision is either on the right or left side of the patient.
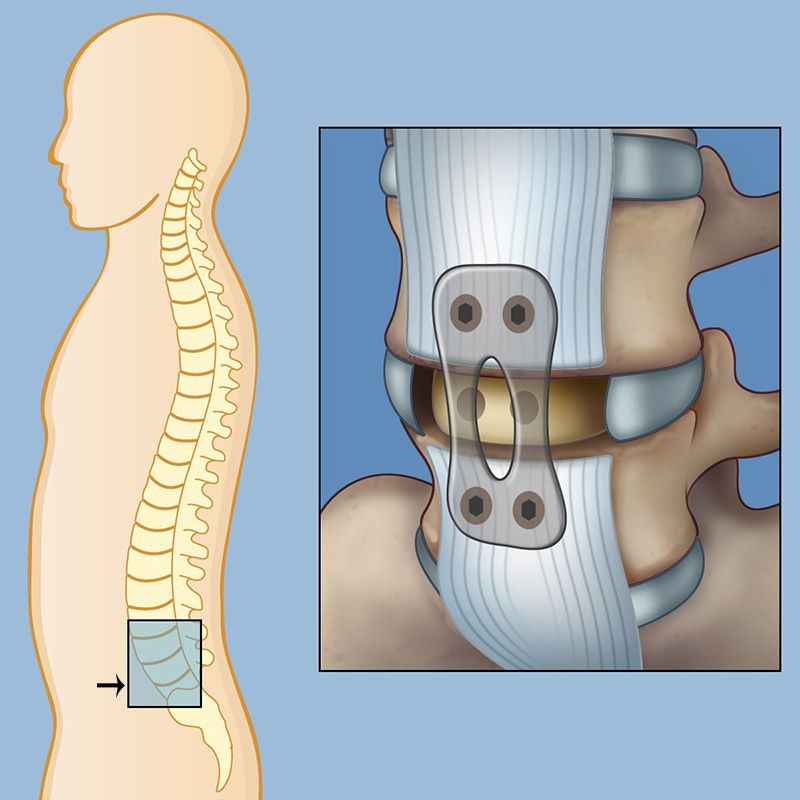
The anterior approach allows a neurosurgeon to insert a larger cage than possible with the traditional posterior (back) approach. The larger cage creates a better curvature to the lower (lumbar) spine, where it is needed for stability and posture. Our spinal surgery experts work alongside specially trained vascular surgeons during the ALIF procedure to safely navigate around the blood vessels in front of the spine.
In most cases, the neurosurgeon uses a posterior approach in addition to the anterior fusion to provide optimal stability.
Not everyone is a good candidate for ALIF. Neurosurgeons identify which patients are candidates for ALIF as opposed to a traditional posterior approach based on a careful physical exam and detailed review of imaging tests.
In an anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) procedure, the neurosurgeon makes the incision on the front (anterior) side of the patient.
TLIF Minimally Invasive Spine Fusion
Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) is an advanced minimally invasive procedure for spinal fusion, in which vertebrae are stabilized to take pressure off nerves and relieve back pain. It is a minimally invasive alternative to older, more invasive methods of spinal fusion, which were more painful and required longer recovery periods. TLIF is performed either through a single midline incision or two very small incisions in the back, so patients experience less pain, shorter recovery times, and fewer surgical complications.
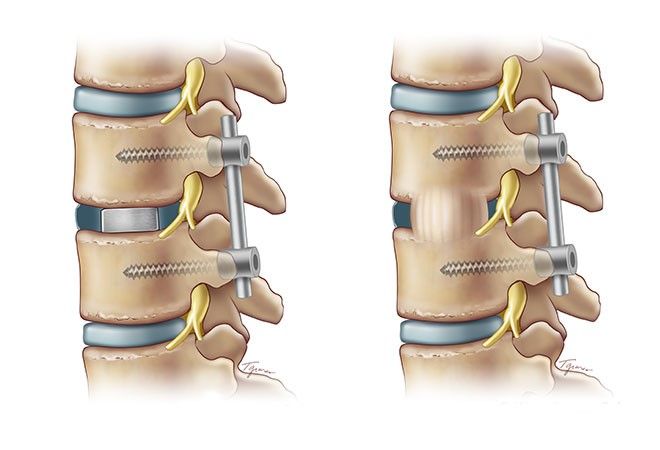
In a spinal fusion procedure, the neurosurgeon inserts a "cage" between the affected vertebrae (left) to restore proper positioning. Six to twelve weeks later (right) bone graft material hardens over the cage, making the fusion permanent.
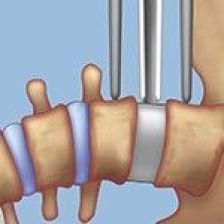
In the LLIF procedure, a neurosurgeon approaches the spine from the side and inserts a spacer to correct curvature.
LLIF (Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion)
Extreme lateral interbody fusion, more commonly referred to as LLIF, is an advanced minimally invasive spine procedure that approaches from the side, avoiding the major muscles of the back. A spine surgeon makes a small incision in the patient’s side between the lower ribs and pelvis, then inserts a special surgical instrument just above the disc space. The surgeon removes the damaged disc tissue and inserts a spacer between the vertebrae. The surgical team monitors the position and correct placement of the spacer, sometimes using special screws or a plate on the side of the spine to offer additional stability. Sometimes small incisions are made in the back for additional screws to optimize stability of the vertebrae as well. Patients typically are walking within a few hours of the LLIF procedure and are then discharged the next day. Most patients are back to work within approximately two weeks.
Reviewed by Paul Park, MD
Last reviewed/last updated July 2024
Illustrations by Thom Graves, CMI