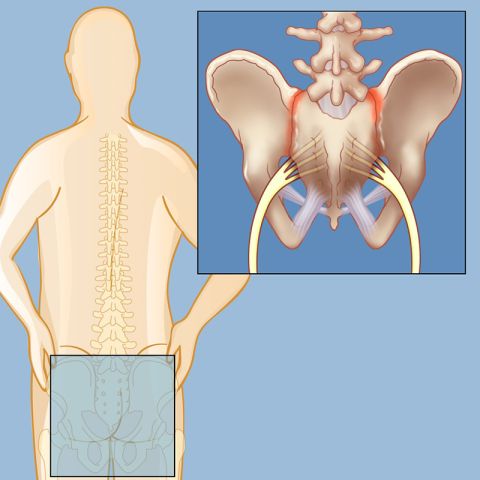
Sacroiliac joint (SI) dysfunction is a condition that results from flawed movement of either one or both of two small, firm joints at the base of the spine. Typically, the sacroiliac joints have a very small range of motion, providing stability when, for example, a person is walking. They also absorb impact and serve the critical role of transferring the weight of the upper body to the lower body.
Hypermobility of the SI joint describes too much movement, which can lead to instability and pain in the lower back and hip that may radiate, or spread. An irritated SI joint can lead to inflammation in the joint, a condition known as sacroiliitis.
The two dimples on a person’s lower back are directly over the SI joints.
SI joint dysfunction is known by other terms as well, such as SI joint syndrome, SI joint disorder, SI joint disease, SI joint strain, and SI joint inflammation.
The SI joints connect the pelvis to the spine through a strong set of ligaments. Specifically, each SI joint links an ilium bone to the sacrum, which consists of five vertebrae that are fused together at the base of the spine. The ilium bones are two large bones that are the uppermost part of the hip bones, which form the main part of the pelvis, and the sacrum sits in the middle.
SI joint pain varies from mild to debilitating, depending on what has led to it. Intense pain can flare up without warning, but the good news is that often the affected joint heals itself within a week or so. It can also last for more than three months, in which case it is considered chronic. The pain may be present all the time or worsen with certain postures or activities.
Sacroiliitis (-itis is a suffix meaning inflammation) can cause low back pain that can be felt on both sides of the back, down through the buttocks, hip, thigh, and back of the legs — similar to the radiating sciatic pain of a herniated or bulging disc. Symptoms may also include fever and stiffness.
What Causes Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction?
Dysfunction in the SI joint is common and can be traced to a range of causes, from autoimmune disorders to osteomyelitis (a bacterial infection of the bone). Causes of SI joint dysfunction include, but are not limited to, the following conditions:
The experts at Och Spine at NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center carefully evaluate each patient to create an individual treatment plan.
Reviewed by: Galal Elsayed, MD
Last reviewed/last updated: September 2023
Illustration by Thom Graves, CMI